Kaizen - Kaizen principle, Kaizen methods & importance for companies
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain...
Modular pipe systems
Attachments
6 min read
![]() Jens Walter
:
29.September.2023
Jens Walter
:
29.September.2023
In today's globalised economy, value creation is a critical factor for companies to differentiate themselves from the competition and achieve long-term success. The ability to create and enhance value through different stages of the value chain is a fundamental principle that helps companies to be profitable and to develop.
In this blog article, we will take a closer look at the concept of value creation and what it means for businesses.
Value creation is the performance of a company to produce products or services that have a higher value than the inputs used. In other words, it is about increasing the value and thus the selling price, and generating profit. To increase the value of a product, companies use raw materials, resources and information.
Value creation includes various activities along the value chain, starting from the procurement of raw materials to the delivery of the finished product to the customer.
Value creation is important because it shows how successfully a company operates and how well it manages its resources to generate profits. Higher value added often indicates better performance of the company.

The concept of value creation is also of importance in economics, as it indicates the economic performance of the country across all economic sectors and industries (= corresponds to the aggregated value creation of all related economic sectors / national accounts). The sum of the value added of all enterprises in an economy forms the gross domestic product (GDP), an important indicator of the economic health of a country.
In this paper, the focus will be on business value added, i.e. the value added by businesses.
Creating value is essential for companies and the economy in general. Here are some reasons why value creation is of high importance:
1. Competitive advantage
2. Profitability
3. Customer satisfaction
Value creation occurs when a company or organisation increases the value of a product or service through its economic activities or services. This usually happens at different stages of the production or service process, i.e. along the value chain. Here are some examples:
Overall, value creation occurs at different stages of the economic life cycle of a product or service as companies use their resources and capabilities to increase value for their customers.

The (gross) value creation is calculated from the difference between the production value and the intermediate inputs. It applies to both companies and the national economy.
Assumed data for the enterprise (manufacture of mobile phones):
Gross value creation is the value created by the enterprise through its economic activities, before all external costs are deducted.
The gross value creation is 700,000 euros. This is the value the company has created by producing mobile phones before wages, operating costs, depreciation and taxes are taken into account.
Net value creation is the amount left over after deducting all costs (including wages, operating costs, depreciation and taxes).
The net value creation is 120,000 Euros. This is the amount that the enterprise has earned as profit after deducting all costs. It is the amount available to make investments, pay off debts or be distributed as profits to the owners.
The value chain is a simple way of describing the different steps or activities that a company goes through to produce a product or service and bring it to market. Each of these steps contributes to the incremental value of the final product.
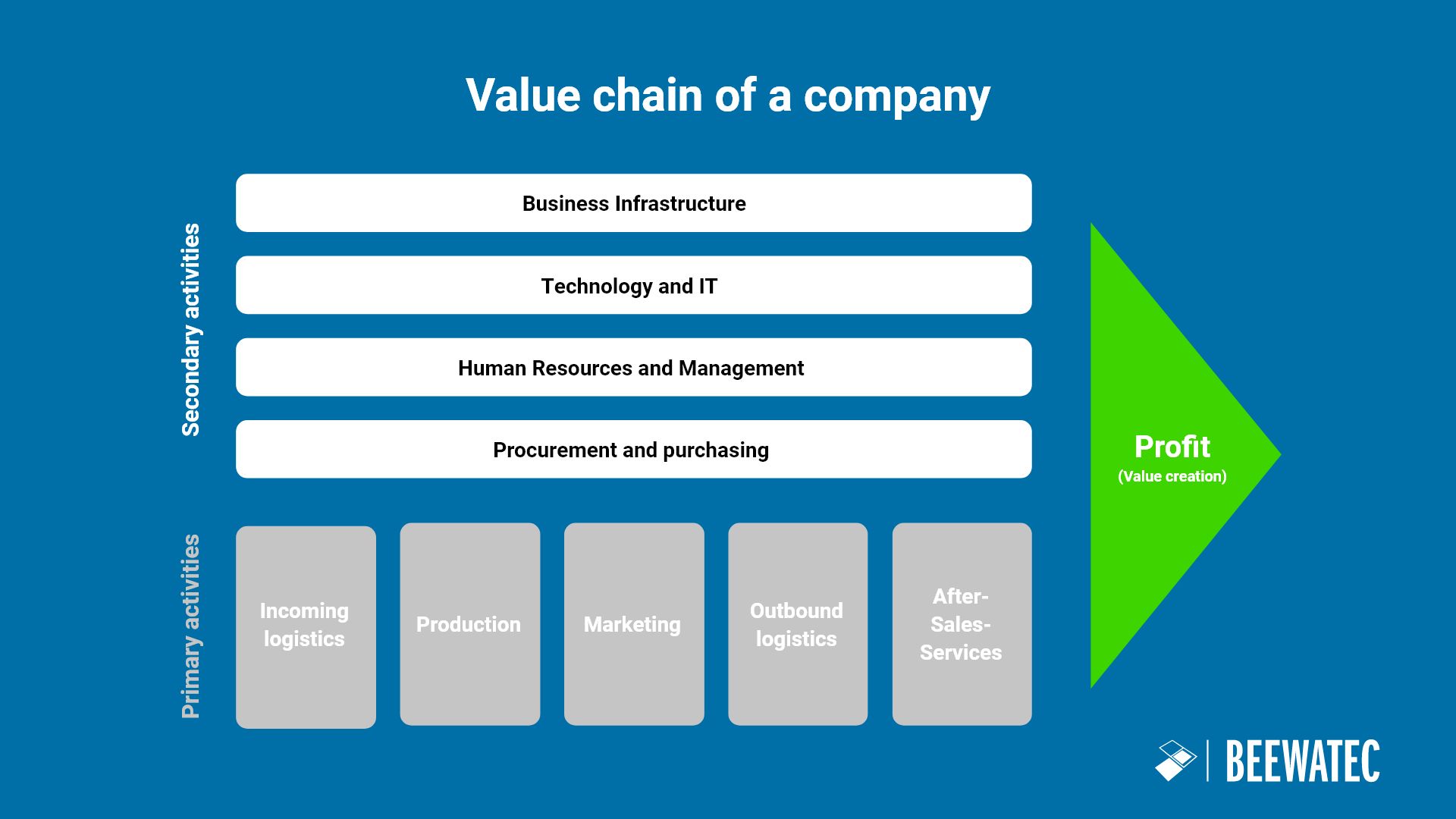
Here is a simple explanation:
The value chain shows how each company carries out a series of activities to incrementally increase the value of a product or service before bringing it to market. This concept helps companies to analyse and optimise their processes to be more competitive and provide more value to customers.
Here is a simple example of a value chain in the food industry, starting with the production of chocolate bars:
In this example, the value chain shows how raw materials are transformed step by step into a final product, namely chocolate bars. Each step helps to increase the value of the product until it is finally sold to customers. This concept can be applied in many different industries to understand and optimise processes to provide more value to customers and be more competitive.
As one of the leading providers of lean systems, we optimise important production factors along the production stages of our customers. Regardless of the industry, our customers benefit from:
_web.jpg?width=600&height=400&name=Beewatec-3-(54)_web.jpg)
Value creation is an essential component of the success of modern companies. By creating value along the value chain, companies can gain competitive advantage, increase profitability and strengthen customer relationships. By using their resources efficiently and focusing on innovation, companies can achieve sustainable growth and long-term success. Value creation is thus a key factor for competitiveness and growth in today's economy.

With our modular system you can implement any solution you need. Discover your possibilities, existing solutions or build your own material flow system with BEEVisio in 3D.
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain...
At a time when companies are striving to increase efficiency and cut costs, the concept of lean management has established itself as a highly...
The material flow is an important part of every production and logistics. It describes the physical movement of materials, products and goods through...